The textile industry, an ancient craft rooted in tradition, is experiencing a profound transformation. For centuries, our looms hummed with human oversight, our dyeing vats followed established recipes, and quality control relied heavily on the keen eyes of experienced professionals. While this human touch has undeniable value, the demands of global markets for speed, precision, consistency, and sustainability are pushing the boundaries of traditional methods. This is where the use of machine learning in textile engineering steps in, offering not just an upgrade, but a complete rethinking of how we design, produce, and manage textiles.
As someone who has navigated the complexities of both traditional textile production and the exciting frontiers of data-driven manufacturing, I’ve witnessed firsthand the challenges and triumphs of integrating advanced analytics. The potential for artificial intelligence to reshape everything from yarn quality prediction to sustainable textile manufacturing is not just theoretical; it’s happening right now on factory floors. This article explores the tangible benefits and practical applications of machine learning in modern textile engineering, offering insights into how these intelligent systems are making our industry smarter, faster, and more environmentally conscious.
Key Takeaways
- Machine learning drastically improves fabric defect detection, offering unparalleled accuracy and efficiency in quality control.
- AI applications optimize complex textile dyeing and finishing processes, leading to reduced waste and superior product consistency.
- Predictive maintenance in textile machinery, powered by AI, minimizes downtime and extends equipment lifespan.
- The impact of artificial intelligence extends to sustainable textile manufacturing, driving resource efficiency and waste reduction.
The Dawn of Intelligent Textiles: Why Machine Learning Matters

Image credit: bernardmarr.com
The textile industry operates on vast amounts of data, often unstructured and underutilized. From raw material properties to production line sensor readings and customer feedback, every stage generates information that can be leveraged. This is precisely where the use of machine learning in textile engineering shines, turning raw data into actionable insights.
Machine learning algorithms can identify patterns, make predictions, and automate decisions at a scale and speed impossible for humans. This capability translates directly into tangible benefits: improved product quality, reduced operational costs, faster time-to-market, and a significant leap forward in sustainability. It’s about moving from reactive problem-solving to proactive optimization across the entire value chain.
Fabric Defect Detection: Sharper Eyes, Smarter Scans

Image credit: www.aeologic.com
One of the most immediate and impactful AI applications in textile quality control is automated fabric defect detection. Traditionally, this was a highly manual, labor-intensive task, prone to human error and fatigue. Inspectors would scrutinize yards of fabric for subtle flaws like broken threads, knots, stains, or weaving inconsistencies.
Today, computer vision for automated textile inspection systems, powered by deep learning, can scan fabrics at high speeds with incredible precision. These systems use cameras and powerful algorithms trained on vast datasets of both perfect and flawed fabrics. They can identify and classify defects in real-time, often catching imperfections that even an experienced human eye might miss. This not only improves consistency but significantly reduces the amount of rejected material, directly impacting profitability.
My own experience with implementing such a system involved initial challenges in data labeling – meticulously categorizing thousands of defect images for the algorithm to learn from. However, once trained, the system’s ability to consistently identify patterns, even in subtly varying lighting conditions, was genuinely impressive, proving invaluable for maintaining high standards.
Optimizing Dyeing and Finishing: Precision in Every Shade

Image credit: journals.sagepub.com
The dyeing and finishing stages are critical for the aesthetic and functional properties of textiles, yet they are notoriously complex and resource-intensive. Achieving consistent color, handle, and performance across batches requires precise control over numerous parameters. Can ML optimize textile dyeing and finishing processes? Absolutely, and with significant benefits.
Machine learning algorithms can analyze historical data, including dye recipes, process parameters (temperature, pressure, time), raw material characteristics, and the final color results. By identifying correlations and predicting outcomes, these algorithms can recommend optimal dyeing and finishing parameters for new batches, minimizing trial and error. This leads to reduced consumption of water, energy, and chemicals, and a dramatic decrease in re-dyeing or reprocessing needs.
For example, a machine learning model might predict precisely how a new batch of cotton, with slightly different absorption properties, will react to a specific dye formula, allowing for real-time adjustments before a single drop of dye is wasted. This level of predictive accuracy is a game-changer for both efficiency and sustainable textile manufacturing.
Predictive Maintenance: Keeping Textile Machinery Running Smoothly

Image credit: www.mdpi.com
Textile manufacturing involves complex machinery – spinning frames, looms, knitting machines, and finishing lines – that operate continuously. Equipment breakdowns can be costly, leading to production delays, missed deadlines, and significant repair expenses. Benefits of predictive maintenance in textile machinery using AI are therefore immense.
Sensors installed on machinery collect vast amounts of data on vibration, temperature, pressure, motor currents, and other operational parameters. Machine learning models analyze this real-time data to detect subtle anomalies that indicate impending equipment failure. Instead of relying on fixed maintenance schedules or waiting for a breakdown (reactive maintenance), AI allows for proactive intervention.
- Identify failing components before they cause a stoppage.
- Schedule maintenance during planned downtime, not during critical production.
- Extend the lifespan of expensive machinery.
- Reduce spare parts inventory by predicting demand more accurately.
I recall instances where unexpected loom breakdowns would halt an entire production line, costing thousands per hour. Implementing a predictive maintenance system, though initially requiring sensor integration and data collection infrastructure, dramatically reduced these unplanned stoppages, shifting our focus from crisis management to strategic operational planning.
Yarn Quality Prediction: Ensuring Strength from the Start
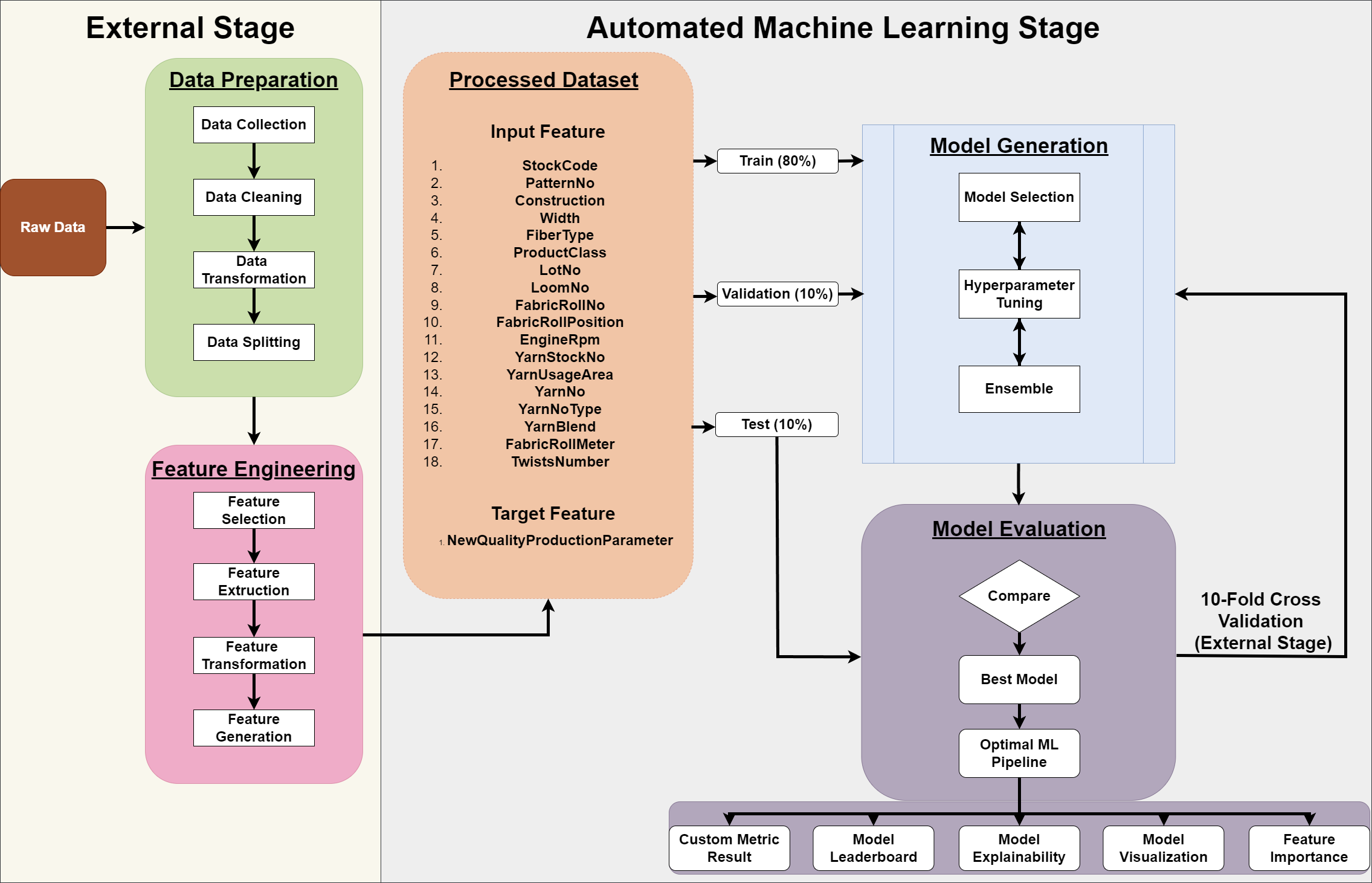
Image credit: peerj.com
The quality of the yarn directly impacts the quality of the final fabric. Factors like fiber length, fineness, strength, and uniformity are crucial. Traditional methods for yarn quality prediction involve laboratory testing, which can be time-consuming and destructive. Machine learning algorithms for yarn quality prediction offer a faster, non-destructive alternative.
By analyzing sensor data collected during the spinning process – such as fiber feeding rates, tension, and spindle speeds – AI models can predict yarn characteristics in real-time. This allows for immediate adjustments to machine settings, ensuring consistent quality and preventing the production of substandard yarn before it even reaches the weaving stage. This proactive quality control is fundamental to improving overall textile quality and reducing waste.
Sustainable Textile Manufacturing: Greener Processes with AI

Image credit: www.icl-group.com
The textile industry faces increasing pressure to adopt more sustainable practices. From reducing water and energy consumption to minimizing chemical use and waste generation, the challenges are considerable. The impact of artificial intelligence on textile manufacturing efficiency extends significantly into sustainability initiatives.
Machine learning plays a crucial role in optimizing various aspects of sustainable textile manufacturing:
- Resource Optimization: AI can predict precise dye and chemical quantities needed, minimizing excess usage.
- Waste Reduction: Improved defect detection and process optimization mean fewer rejected products and less material waste.
- Energy Efficiency: AI models can optimize machine operation schedules and settings to consume less energy during peak and off-peak hours.
- Traceability: Blockchain integrated with AI can track materials from source to finished product, enhancing transparency and ethical sourcing.
For a deeper understanding of the broader implications of AI in sustainable industries, consider consulting reputable environmental technology reports or academic publications, such as those found on sites like ScienceDirect or university research portals.
Data Science in Textile Process Optimization: Beyond Intuition
Image credit: kanerika.com
At its core, the use of machine learning in textile engineering is an application of data science. Modern textile factories generate vast amounts of operational data from sensors, production logs, quality checks, and inventory systems. Traditionally, much of this data went unanalyzed, or insights were derived from manual, retrospective reviews.
Today, real-time data analysis in textile engineering with AI allows manufacturers to move beyond intuition and make data-driven decisions. Data science in textile process optimization involves collecting, cleaning, and analyzing this data to identify bottlenecks, optimize production flows, predict demand, and fine-tune machine parameters. This holistic approach ensures that every part of the production line is working at peak efficiency.
AI applications for optimizing spinning and weaving parameters, for example, can dynamically adjust machine settings based on changes in raw material properties or environmental conditions, maintaining optimal output and quality.
Challenges and the Road Ahead: Implementing AI in Textile Production

Image credit: www.ultralytics.com
While the benefits are clear, implementing AI in textile production lines comes with its own set of challenges. From my vantage point, the initial investment in technology – sensors, high-performance computing, and specialized software – can be substantial. Integrating legacy machinery with new AI systems also often presents significant engineering hurdles.
Another critical aspect is data quality and availability. Machine learning models are only as good as the data they are trained on. Dirty, incomplete, or inconsistent data can lead to skewed predictions and ineffective solutions. Furthermore, there’s a need for a skilled workforce capable of developing, deploying, and maintaining these AI systems, which often requires upskilling existing staff or hiring new talent with data science expertise.
Despite these hurdles, the trajectory is clear. The advantages in efficiency, quality, and sustainability make the adoption of machine learning an inevitable and necessary step for textile engineering firms looking to remain competitive in the global market. Collaborations between technology providers and textile manufacturers are crucial for overcoming these challenges and unlocking the full potential of AI.
For more detailed insights into the specific technological and economic challenges of AI adoption in manufacturing, reliable resources such as reports from the World Economic Forum or academic journals on industrial automation can offer comprehensive perspectives on the subject.
Frequently Asked Questions
Image credit: www.mdpi.com
How does machine learning improve fabric defect detection?
Machine learning, particularly through computer vision, uses algorithms trained on extensive datasets of fabrics to identify and classify defects in real-time. This automated textile inspection process offers higher accuracy and consistency than manual inspection, significantly reducing human error and improving overall quality control.
What are the primary AI applications in textile quality control?
Beyond fabric defect detection, AI applications in textile quality control include real-time yarn quality prediction, color consistency matching in dyeing processes, and identifying anomalies in production data that might indicate a quality issue. These applications ensure a higher standard of product from raw material to finished good.
Can ML optimize textile dyeing and finishing processes?
Yes, machine learning can significantly optimize textile dyeing and finishing processes. By analyzing historical data and real-time parameters, ML algorithms predict optimal dye recipes and process settings, leading to reduced chemical, water, and energy consumption, while achieving greater color accuracy and consistency across batches.
What are the benefits of predictive maintenance in textile machinery using AI?
The benefits of predictive maintenance are numerous: it reduces unplanned downtime by anticipating equipment failures, allows for proactive maintenance scheduling, extends the lifespan of machinery, and optimizes spare parts inventory. This minimizes production disruptions and lowers operational costs significantly.
How does the use of machine learning contribute to sustainable textile manufacturing?
Machine learning supports sustainable textile manufacturing by optimizing resource use (water, energy, chemicals), reducing waste through improved defect detection and process efficiency, and enabling more precise control over environmentally impactful processes like dyeing. This leads to a smaller environmental footprint and more responsible production.





Leave a Reply